Welcome to the exploration of the world of hope theory. In this article, you will learn what hope is and how it plays an integral part in the development of your psychological state. By exploring Snyder’s hope theory, you will uncover the three essential components that drive hope: agency, pathways, and goals.
Do not worry if these terms do not sound familiar to you at the moment. In the near future, they will become a part of your emotional toolkit. By the end of this article, you will be able to rise from ashes to glory, understand better how to implement theory of hope into your everyday life to deal with adversity, and develop a stronger sense of hope, willpower and optimism. Cheer up! This is where your journey to a better future begins.
Table of Contents
What is the Concept of Hope?

Is Hope an Emotion?
Hope is not simply a feeling or a sentiment; hope is a way of thinking. This is the process of expecting good results that stem from establishing goals and motivation. It is important to note that although hope can involve certain emotions such as optimism, hope is, at its core, a cognitive process that infers a better future is achievable.
Hope Psychology
Hope psychology seeks to understand the extent to which hope influences the behavior, thought processes and psychological well-being of individuals. It focuses on how people create and work towards goals, how they manage to achieve those desirable goals, and why hope is essential to maintaining good coping strategies. Studies in hope psychology reveal hope as a valuable predictor of success and life satisfaction.
Hope Theory by Snyder
Overview of Snyder’s Hope Theory
According to Snyder’s hope theory, hope can be defined in the context of cognitive-motivational theory. In this theory, hope is defined as a state that stems from personally constructed sense of self-belief, especially in relation to goal imagery and planning.
According to Snyder, hope encompasses both the drive toward goals and the capacity to fulfill strategies for reaching those goals. Agency and pathways distinguish hopeful people from those who have intentions toward goals but do not know effective ways of getting there or from those who know how but lack motivation and willpower.
What Are The Three Components of Hope Theory?

1. Agency
- The agency is a motivational aspect of hope.
- It symbolizes a person’s perception of his or her ability to start and maintain processes toward achieving specific life outcomes or goals.
- Higher agency is characterized by purpose and assertiveness, or the degree to which an individual believes he or she can work through obstacles and shape life outcomes.
- It encompasses the self-belief that an individual is in charge and possesses the ability to shape the current and future life.
2. Pathways
- Pathways reflect the preparatory aspect of hope.
- This includes the capacity to create different paths to accomplish plans and to recognize effective approaches to managing real challenges.
- High pathway thinking entails the capacity of an individual to come up with many strategies for achieving objectives and then find ways of dealing with the challenges in case they arise.
- It involves the ability to think flexibly and come up with other different approaches when things do not pan out as expected.
3. Goals
- Goals are the final points or objectives that people set in their course of action.
- Goals give directions, and they are the outcomes of agency thinking and pathway thinking.
- Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals are essential for hope because such goals provide an actionable and tangible road map to work towards.
- Goals are the key to motivation as they establish the focus that keeps people and their minds moving toward the desired direction.
Read More: The Ultimate Guide To S.M.A.R.T. Goals
Hope Model
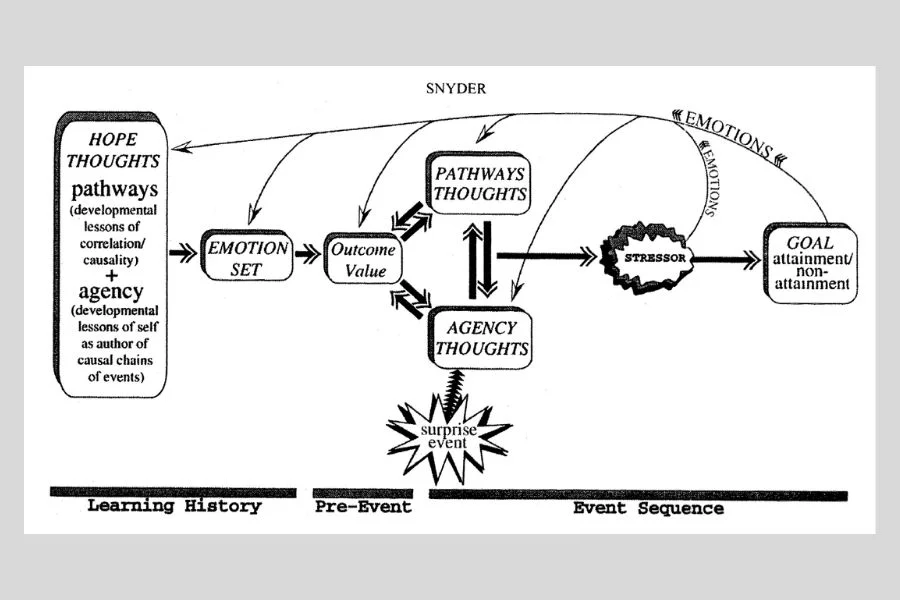
Here are the critical points from Snyder’s Hope Model:
- Pathways and Agency Thinking: Acquired in childhood and further on, these shape how people approach objectives.
- Emotional Sets: While high-hope people show positive affect, such as joy and optimism, low-hope people demonstrate negative affect and self-pessimism.
- Goal Generation: High-hope people are likely to create more goals, which helps build up more excellent resources for overcoming obstacles and adjustment in goal striving.
- Outcome Value Appraisal: People evaluate the significance of goal outcomes before investing in cognitive effort.
- Emotional Influence: Emotions regulate cognition and operate as functional states that support the enhancement of goal-oriented behavior.
- Stress Response: High-hope people believe stressors are opportunities, aligning their pathways and agency to the stressors.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Feelings and perceptions about goal accomplishment relate to future goal setting and strategy enhancement.
- Surprise Events: External stimuli may trigger explicit emotions affecting subsequent goal striving.
- Hope Model Dynamics: They incorporate feedback (anticipatory) and feedback (evaluative), hence improving goal pursuit efficiency.
Related Reading: Cognitive Triad: Enable Growth with Essential Insights
Hope Theory Example
Emily is a high school student who is facing several challenges, including low academic performance and low self-esteem. As a result, her school counselor introduces her to theory of hope. Emily defines tasks for her studies and options for accomplishing them and develops self-belief.
With this kind of support, Emily’s school performance is significantly boosted by the end of the semester. She adopts good study strategies, gains confidence, and participates more in class activities. Thus, not only does Emily show improved academic performance, but she is also happier and has a greater sense of self-worth, which further reinforces the theory of hope.
Hope Theory in Positive Psychology

How Hope Theory Contributes to Positive Psychology
Hope Theory is a fundamental theory of positive psychology. It advances the concept of human strengths and overall psychological well-being rather than studying only disease. Theory of hope does this by offering a framework for developing optimism and determination. It focuses on goals, pathways, and agency, which are paramount when it comes to creating optimism and proactive behavior.
Advantages of Incorporating Hope Theory into Psychological Models
The benefits of Incorporating theory of hope in the psychological paradigms include the following:
- It offers a tangible way of developing strength and ways of handling stress, which is crucial to psychological well-being.
- Clients can use it to state desirable goals, identify on how they can surmount challenges, and stay motivated.
- It may result in better results in therapy, like an increased level of life satisfaction, a better strategy for coping with stress, and less prevalence of symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Related Reading: Cognitive Evaluation Theory: How It Helps You
Hope Theory: Rainbows in the Mind PDF
“Hope Theory: Rainbows in the Mind” is a pioneering study by C.R. Snyder aimed at the theoretical understanding and empirical investigation of hope as a cognitive-motivational disposition. The phrase “rainbows in the mind” provides a colorful and diverse concept of hope that suggests it can paint one’s mind with optimism.
Examples of Hope
Historical examples are particularly vivid and impressive, illustrating that hope can work a miracle. One example is Nelson Mandela’s optimism throughout his 27 years of imprisonment under South Africa’s apartheid system of governance. Mandela remained optimistic about the change and equality for black people throughout his struggle and practice of a non-racial society, which demonstrated how hope is able to uphold a nation even in the face of tremendous hardships.
Another example is the Civil Rights Movement in America, where various icons, such as Martin Luther King Jr. , signified hope in the attainment of racial integration. In his iconic ‘I Have a Dream’ speech, he roused millions, showing how hope motivates people to push for social change.
Hope Ted Talk
Why is Hope Important?
Benefits of Hope ( The Power of Hope )
The power of hope is discussed below:
- Psychological Resilience: Optimism helps one overcoming obstacles and remain strong even when going through tough times. It gives hope, enabling people to endure difficult moments rather than quit.
- Emotional Well-being: Instead of leaving the mind helpless and desperate, hope brings freedom and gives it a positive focus. It can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety by increasing a sense of purpose or a positive outlook toward the future.
- Health Benefits: It also points out that optimism may be associated with improved physical health outcomes in people. They may adopt proper health measures like exercising and seeking medical attention for checkups, hence enhancing their health.
- Motivation and Goal Achievement: Hope motivates people to work hard and maintain long-term focus because it focuses on the positive outcome that is expected in the future. It challenges people to endeavor and attempt to achieve the needed goals, hence enhancing productivity and character building.
- Social Connection: It is believed that hope enhances social interactions and interpersonal relationships because hopeful people will always have a positive perception of social interactions. It fosters knowledge or acceptance and also makes encouragement.
- Coping with Uncertainty: In a time of ambiguity, hope brings a sense of control over the circumstances. It helps individuals cope with the state of ambiguity and make decisions while at the same time exercising optimism.
Related reading: Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide
Strategies to Apply Hope Theory in Daily Life
Using theory of hope in practice can work wonders because it deals with goals, pathways, and agency. Here are some practical strategies:
- Set Realistic Goals: Encourage the setting of challenging but realistic sub-objectives. This approach also keeps one motivated and gives one direction on what one wants to achieve.
- Develop Multiple Pathways: When problems arise, consider how you can achieve your goals. Creativity and openness enable people to overcome challenges and continue on their chosen path.
- Monitor Progress: This means keeping track of your achievements and the changes you make along the way. This assists in maintaining motivation and provide insights into what strategies are effective.
- Seek Social Support: Share your goals and achievements with positive role models such as friends, family, or coaches. They can motivate you and help you see things from a positive angle, enabling you to achieve your dreams.
- Cultivate Optimism: Positive thinking aids in building up a resistance mechanism and problem-solving skills.
- Use Imagery and Visualization: See yourself attaining your objectives and achieving your set goals. This process can motivate and inspire you to achieve your dreams and goals.
- Take Action: Commit yourself to tasks that will help you achieve your goals and objectives. Taking the initiative promotes assertiveness and confidence in being able to cause change.
- Learn from Setbacks: It is also essential to view events more as learning experiences rather than failures. Evaluate what went wrong and modify your approaches, which encourages adaptive thinking.
- Celebrate Achievements: Take time to note achievements as you progress through the process. This helps propel progress and motivates you to be on the chosen track.
- Practice Self-Compassion: When you face a challenge or a setback, be gentle with yourself. Self-compassion enables one to remain optimistic during tough periods in life.
Conclusion
When discussing hope theory, we have looked into hope’s definition as not only an emotion but a complex psychological concept vital for human development and coping. Snyder’s hope theory posits three pivotal components: agency, pathways, and goals, which enable people to overcome obstacles and achieve their purpose.
This is because theory of hope is critical in positive psychology as it enriches frameworks with such a transformative aspect. Examples from history, such as Nelson Mandela and Martin Luther King Jr. , elucidate how it can help instill tenacity and bring about remarkable results. Incorporating hope in daily practice fosters a positive expectation, optimizing goal pursuit and coping in the face of emerging challenges.
Pro-Tip From Basics of Psychology
Thus, growing hope as a cognitive and emotionally driven concept may enhance its effectiveness in promoting long-term optimism and persistence. Learn from failures as they are learning experiences that can be used to create more effective strategies for success while believing in the possibility of success.













