Explore the personality and work of ‘Richard Lazarus’, a famous psychologist who is known for his revolutionary insights about stress, coping, and emotions. This article will take you on an interesting trip through the life of Lazarus, who is best known for his influential theories.
The theories of ‘Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’ on stress and coping will be disclosed in the article, making the difference between problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies clearer on the one hand. Employing vivid illustrations, the post illustrates ‘Lazarus model of stress’ which is comprised of cognitive appraisal, emotional appraisal, and coping strategies.
Take on a more profound grasp of ‘Richard Lazarus cognitive mediational theory’ where he delves into the complex interrelatedness between cognitive assessment and emotional experiences. Through vivid illustrations, readers will acquire a deeper understanding of the impact of Richard Lazarus’s work as it relates to psychology, health, and stress management. Let’s do this together to unravel the enduring legacy of human behavior and emotion, which were shaped by Richard Lazarus.
Table of Contents
Biography of Richard Lazarus
Early Life
Richard Lazarus was born on the third day of March 1922, in the city of New York. Lazarus experienced a formative period during the Great Depression when his interest in psychology was spurred by the difficulties of his family and community. His early encounters sparked his interest in human behavior and emotion and created the basis of his future profession in psychology.
What Did Richard Lazarus Study?
Lazarus continued his education at City College of New York where he graduated with a degree in psychology. He next went to ‘Harvard University’ where he received his Ph.D. in psychology in 1951. Lazarus spent his years at Harvard surrounded by psychology figures like Gordon Allport and Henry Murray who influenced his research focus on emotions and stress.
Career Journey as a Psychologist
Later on, Lazarus started a brilliant career that was connected to teaching and practice. While teaching at highly rated institutions such as Clark University and UC Berkeley, he engaged in research of cognitive aspects of emotion and stress. Creating the ‘Lazarus cognitive mediational theory’, Lazarus brought in an aspect of appraisal that changed the perspective of emotion psychology.
Notable Achievements and Awards
Lazarus is well recognized for his pioneering contributions to psychology. He received an Award for Distinguished Scientific Contribution from APA and a Lifetime Achievement Award from APS. His work on emotion theory, stress, and adaptation, brought him renown as 20th century foremost psychologist.
What is Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’s Theory of Stress and Coping?
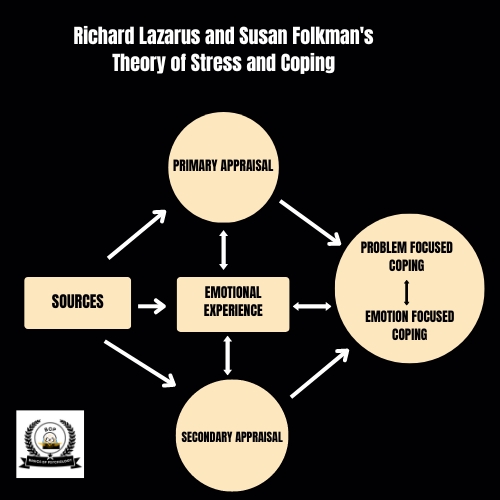
Overview of The Theory
Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’s stress and coping theory is seen as a foundation in the psychology field, mainly because it helps explore and explain how people deal with stressful circumstances.
‘Richard Lazarus theory of stress’ says that when persons feel they have few coping resources to deal with the stressful situation, the stress occurs. The notion of unbalance in demands and resources is born which sets off a stress response followed by employing coping mechanisms to restore normalcy.
What Is Problem-Focused Coping (Richard Lazarus)?
Problem-based coping (as defined by Richard Lazarus) requires that the stressor is addressed immediately and dealt with. People using this coping strategy have the goal to change the inner conditions of stress or to increase their ability to handle these circumstances properly. This is the representation of faith in one’s ability to shape and control the surrounding environment.
What Is an Example of Problem-Focused Coping?
Imagine a person who faces job stress caused by an intense workload. To deal with this stressor they might use situation-oriented strategies like organizing the tasks, delegating responsibilities, or taking more training to increase efficiency. Through dealing directly with the stress source they aim to regain equilibrium and diminish the influence of the stressor on their mental health.
What Is The Difference Between Problem-Focused and Emotion-Focused Coping?
Problem-focused coping aims to deal with the actual stressor, but the purpose of emotion-focused coping is to deal with emotional reactions instead.
Emotion-focused coping tactics seek to manage and relieve the distressing emotions that are triggered by the stressor without this always having a direct effect on the external environment. Emotional support, relaxation methods, or distraction ways can be provided as well for instance.
Is Problem-Focused Coping Best?
Many factors including the type of stressor, individual preference, and availability of resources can influence how problem-focused coping works. The problem-focused coping is especially helpful in cases when the stressor is controlled and can be changed through direct action.
On the other hand, when the stressor is beyond one’s control, emotion-focused coping may be more helpful as it helps people control their emotional reactions and adapt to the situation.
What Are The Coping Strategies of Lazarus and Folkman?
These researchers emphasized the existence of various coping mechanisms that individuals use to control stress, sadness and fear. These tactics involve problem-oriented methods dealing with the stressor or one’s relationship with it and emotional methods aiming at controlling emotional responses.
What Are The 5 Main Types of Coping Skills?
Common coping strategies are given in the table below:
| Problem-Solving | Identifying practical ways that directly address the stressor. |
| Seeking Social Support | Turning to friends, family, or coworkers for help, guidance, or comfort. |
| Positive Reappraisal | Presenting the circumstance in a more positive or meaningful perspective to diminish its perceived significance. |
| Avoidance | Temporarily removing oneself from the stressor or avoiding stressful situations. |
| Acceptance | Acknowledging the presence of the stressor and taking a nonjudgmental, accommodating approach to it. |
What Is The Psychological Stress Model Developed By Richard Lazarus?
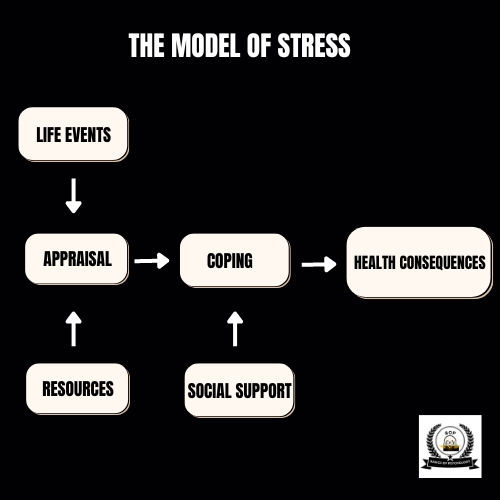
‘Richard Lazarus model of stress’ offers a complete framework for understanding the stress response, including cognitive, emotional, and behavioral elements.
What Are The Three Elements of Lazarus Model of Stress?
At its core, the model emphasizes three interrelated elements which are discussed below:
Cognitive Appraisal
People go through a cognitive assessment process to evaluate the gravity of stressors concerning their well-being. This appraisal involves two primary components: primary evaluation, an initial assessment of its relevance and importance, and secondary appraisal, which appraises one’s resources and options.
Stress Appraisal
Stress appraisal implies the way people view their competencies in handling the stressors demands. These psychological consequences affect their emotional and physical reactions to the event and how they deal with it.
Coping Strategies
Stress management is achieved, using cognitive and emotional resources through coping methods. These strategies can be typified by problem-solving coping that is targeted to the stressors themselves or emotion-directing coping that focuses on the emotions of stressors.
Richard Lazarus Stress Theory

Cognitive Appraisal in Stress Theory
According to ‘Richard Lazarus theory of stress’, the specific facet involves the cognitive assessment that people make in response to stressful circumstances. It involves the appraisal of the importance of the stressor and the ability to cope with it.
Primary Appraisal
At first, cognitive evaluation of the stressor’s relevance to one’s welfare ensues. People rate the situation as a threat, challenge, or no challenge. e.g., a job interview can be tricky in two regards: it might be exciting because it provides an opportunity for growth; or else, it may evoke anxiety of failure.
Secondary Appraisal
Secondary assessment is about assessing one’s coping resources as well as the options that are available to deal with the stressor. People decide whether they have the resources and competencies to deal successfully with the situation or not. This evaluation shapes their emotional and behavioral reactions to stress.
Coping Strategies
According to ‘Richard Lazarus’, the coping strategies that individuals use to deal with stress may differ. Problem-oriented coping entails active steps to counteract with the stressor, e.g., problem-solving or seeking social connection. Emotion-focused coping seeks to moderate emotional reactions to stress, using methods like seeking support or relaxation techniques.
Example
Picture a student who has an exam coming up. Via primary appraisal, individuals consider the test as difficult but doable. Another factor is secondary appraisal when they evaluate their coping resources such as study materials and support from peers. They encounter the problem-focused coping style by creating a study schedule and seeking help from a tutor, while the emotion-focused style is by practicing relaxation techniques to manage test anxiety.
Richard Lazarus Appraisal Theory

Role of Cognitive Appraisal in Emotion
‘Richard Lazarus appraisal theory’ is based on cognitive aspects of emotion. Considering them, emotions are not direct responses to stimuli but are rather guided by cognitive assessments of them.
Primary and Secondary Appraisals in Emotion
Likewise, Lazarus suggests primary and secondary appraisals as in emotion. At the primary appraisal stage, one assesses the importance of the event to one’s well-being as well as if it supports one’s goals and beliefs. The next step is appraising the secondary one in which an individual evaluates the ability to cope with emotional experience as they assess the available coping resources.
Example
Imagine an employee who has just been given some critical feedback at their workplace. Their tendency to assess as a threat to their competence and self-esteem is called primary appraisal. During the process of secondary appraisal, they decide whether they use coping skills such as asking for clarification or support from others. As a result of these evaluations, they can end up feeling angry or stressed.
Emotion Regulation Through Appraisal
‘Richard Lazarus’ refers to cognitive appraisal processes that regulate emotions. Through actively interpreting and revising emotional instances individuals can modulate their emotional reactions. When appraisals are positive, chances are they will determine adaptive emotional responses and when appraisals are negative, they may aggravate emotional problems.
Example
People can control their emotions during tough circumstances, say, public speaking by reshaping the situation as an opportunity rather than a perceived danger. Thus, cognitive restructuring not only reduces anxiety but also increases performance.
Richard Lazarus Theory of Emotion

How Does Lazarus Explain Emotions in Psychology?
Richard Lazarus argues for a memorable emotional theory that underscores the vital role appraisal plays in determining feelings. In light of Lazarus’ theory of emotion, emotions are not direct reactions to the stimuli but are rather the interpreted and evaluated occurrences by individuals. The relevance of the events to one’s well-being, determined by these cognitive appraisal processes, produces definite emotional responses.
Cognitive Appraisal’s Role in Emotion Regulation
The main principle in ‘Richard Lazarus theory of emotions’ is that cognitive appraisal processes are important in regulating emotions. Through the process of analyzing and re-evaluating stressful or emotionally arousing situations, individuals can adjust their emotional patterns and flexibly deal with demanding circumstances. Positive appraisals tend to improve the prospects of favorable emotional states, however, negative appraisals aggravate emotional responses.
Relationship Between Emotion and Stress Appraisal
Richard Lazarus emphasizes the mutual connection between Emotion and Stress appraisal, and thus, underscores the magnitude at which these interact in the stress process. Individuals’ appraisals of the stressor are not only based on emotions but also the other way around.
Say, for example, the personal appraisal of resources and efficacy of cognitive capacity can modulate the intensity and nature of stress, providing evidence on the dynamics between cognitive appraisal, emotion, and stress.
What Is an Example of The Richard Lazarus Theory?
The principled case of the application of ‘Richard Lazarus appraisal theory’ in practice is when an individual faces a possibly outflowing situation, for instance, a job interview. In this case, the person’s initial evaluation of the context as either not dangerous or scary shapes their corresponding emotional and physiological reactions. Afterward, the cognitive appraisal model on how they cope with testing during the interview further develops the emotional experience and behavioral responses.
Richard Lazarus Contribution to Psychology
Focus on Health Psychology and Stress Management
Richard Lazarus, a psychologist worth mentioning, introduced important ideas in the field of health psychology and coping with stress. His study investigated how individuals perceived and used resources when stressed, thus foreshadowing the elements of ‘Richard Lazarus theory of stress’.
Richard Lazarus presented stress as essentially subjective by saying that it is not the event that causes it by itself but the way the event is appraised. This involves looking at the intensity of stressors and the body’s ability to cope with them thus shaping the emotional and physiological responses. Through examination of these mechanisms, Lazarus extended the knowledge of why and how stress affects health, happiness and well-being.
Impact of Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’s Work on Coping Strategies
‘Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’ jointly formulated the Transactional Model of Stress and Coping, which has been widely used. This model underlines the fact that coping is a continuous transaction between an individual and the environment.
The core of their theory is the difference between problem-oriented coping (aimed at altering the stressor itself) and emotion-directed coping (focused on managing the emotional reactions towards the stressor).
Their research brought up several methods of adoption by people like seeking social support, redesigning the situation, or problem-solving. Additionally, they focused on the adaptive nature of coping, demonstrating its ability to mitigate the harmful effects of stress on mental and physical health.
‘Richard Lazarus and Susan Folkman’ were pioneers in the field of coping strategies, highlighting the significance of individual differences in coping success. Their work laid the groundwork for the intervention mechanisms in health psychology, which aimed at enhancing coping skills to minimize the negative impact of stress on health.
Through exposure to the complex interplay of cognition, emotions, and behavior in stress management, Richard Lazarus’s legacy lives on in formulating modern practices of health and resilience under adversity.
Richard Lazarus Quotes
Some of the famous quotes by ‘Richard Lazarus’ are given below:
“Stress is not what happens to us. It’s our response to what happens. And the response is something we can choose.”
“Emotions are not reactions to the world; they are our constructions of the world.”
“If we wish to understand the nature of emotion, we must understand the nature of all the events to which emotions are responses.”
“Stress occurs when environmental demands tax or exceed the adaptive capacity of an organism, resulting in psychological and biological changes that may place persons at risk for disease.”
“Coping with stress is not magic. It requires hard work, creativity, trial and error, and practice.”
Richard Lazarus Books
Some of the Richard Lazarus’ famous books are given in the table below:
| “Psychological Stress and the Coping Process” (1966) | A classic text that explains Richard Lazarus’ transactional model of stress and coping. |
| “Stress, Appraisal, and Coping” (1984) | Investigates cognitive appraisal’s function in molding people’s responses to stress. |
| “Emotion and Adaptation” (1991) | Explains the nature of emotions and their adaptive purposes. |
| “Coping with Aging” (2000) | Investigates psychological elements of aging and coping techniques for older persons. |
Conclusion
In summary, the biography of Richard Lazarus depicted not only an academic trailblazer but also a revolutionary psychologist whose legacy endures to this day. Working together, Folkman and Selye came up with a key theory on stress and coping, characterized by problem-oriented and emotion-focused approaches.
Through the careful examination of Lazarus’ model of stress and Richard Lazarus’ appraisal theory, the readers got an understanding of the intricate interrelationships between cognition, emotion, and stress.
The importance of problem-focused coping became more apparent as the examples unfolded, here readers would be given feasible tools for overcoming difficult situations. The impact of Lazarus on contemporary psychology is strongly manifested in his work in health psychology and its application to stress management, which paved the way to the current understanding and interventions.
Throughout their hike of Richard Lazarus’ theories and contributions, readers become endowed with an in-depth understanding of coping mechanisms, stress appraisal, and emotion regulation which promote resilience and well-being in challenging contexts.
Through his fundamental contributions to psychology, he set the stage for breakthroughs in stress management and mental health strategies. By using his research and teaching, Lazarus not only clarified the intricacies of human emotions and survival but also provided a methodology for individuals to cope with life’s difficulties more effectively and aware.













