Are you ready to explore the universe of BF. Skinner? Who was one of the most prominent psychologists of the twentieth century? In this article, the reader will learn about Skinner’s revolutionary theories and how they are still applicable today. You will discover his life, the establishment of behaviorism, and the groundbreaking idea of operant conditioning. Understanding Skinner’s work will enlighten you about the factors that influence learning and how these principles are used in education and, therapy, and other settings.
Fear not; by the time you’re done with this article, you’ll be well-prepared to view the world through the lens of Skinner. Get ready to change the way you look at people by turning the page!
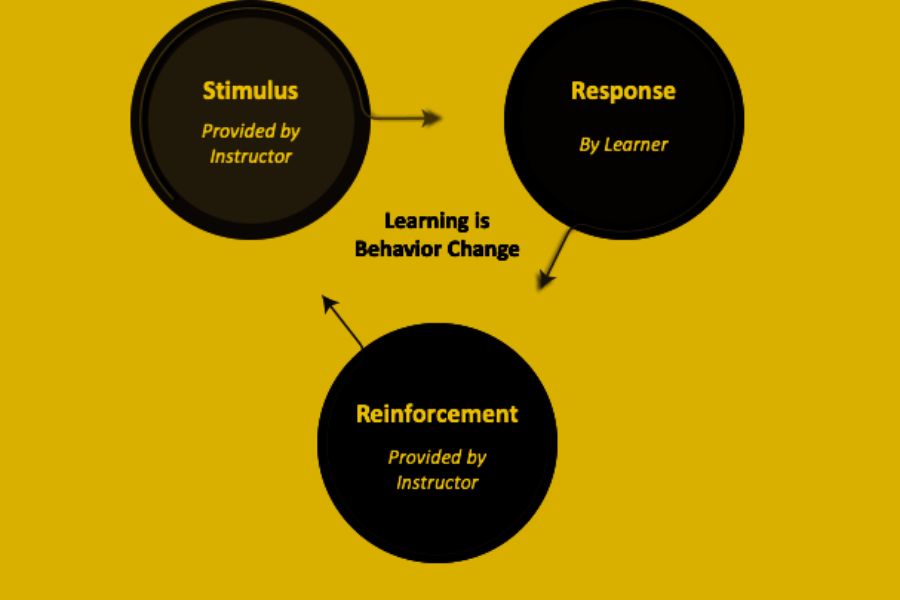
Table of Contents
A Brief Overview of BF. Skinner’s Significance in Psychology
He is universally regarded as one of the most preeminent psychologists ever known, leaving behind him a body of work that encompasses both Behaviorism and Radical Behaviorism.
He was pivotal in forming various pioneering psychological theories, which increased our perception of human behavior and created a pathway for further research into numerous facets of psychology, such as operant conditioning, reinforcement theory, cognitive learning theory, and more.
Furthermore, he had an essential role in altering society’s views on education by introducing novel approaches centered around personal development rather than traditional techniques like rote learning or memorization, which were typically employed at the time.
Even though he passed away over two decades ago, his impact is still being felt today across multiple branches of psychology, including clinical practice, educational studies & teaching procedures, and even pop culture, with his work motivating many movies & television series throughout the years as well as influencing different areas outside of psychology such as marketing & economics among others.
BF. Skinner’s Life and Theories
Early Life and Education of BF. Skinner
Birth and Family Background in Susquehanna, Pennsylvania
BF. Skinner was born to William and Grace Skinner on March 20, 1904, in Susquehanna, Pennsylvania. His father had served two terms as a legislator for the state, while his mother greatly admired literature of any kind. Two younger brothers – Edward and Harold – also succeeded in their respective disciplines later in life.
Academic Excellence and Early Education
In his youth, his academic excellence allowed him to skip several grade levels ahead of his peers. He ultimately attended Susquehanna University at the age of fourteen after initially starting with the local public schooling system.
As an undergraduate student at the university, he majored in English Literature; however, during his senior year, he opted to switch majors and graduated with a degree in Psychology instead in 1926. Following graduation from college, he enrolled at Harvard University, where, under Professor Roger Sperry’s mentorship, He earned his Ph.D.
At Harvard, Skinner commenced experiments on animal behavior, which spawned the development of one of the most influential theories concerning operant conditioning – also known as “Skinner’s box.” This theory suggests that behavior is dictated by its repercussions; positive reinforcement will cause an increase in a given behavior, while negative reinforcement shall reduce it if endured for an adequate amount of time due to either reward or punishment being associated with it.
The theory of Radical Behaviorism, developed by B.F. While studying at Harvard University, Skinner has been widely applied within the realm of Psychology and in many other scientific disciplines, such as Education and Management Training Programs, since its publication in the Psychological Review journal article back in 1938. This theory proposes that human behavior is determined entirely by environmental factors rather than internal stimuli like thoughts or emotions; thus, all behavior can be explained through observable causes rather than subjective ones with no mental processes existing outside those that may be directly observed via external reactions.
The Founding of Behaviorism
Overview of Behaviorism as a Psychological School
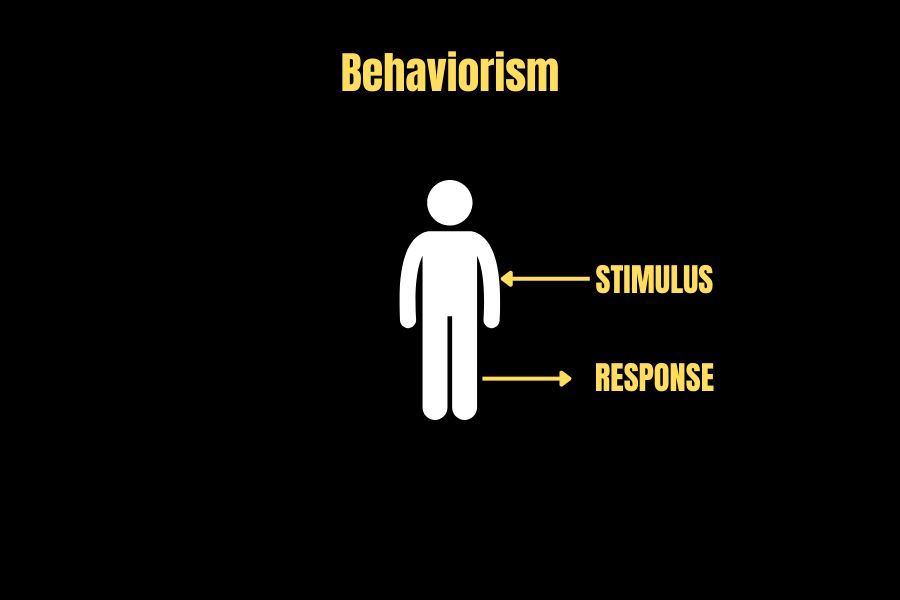
In the 1920s, BF. Skinner founded behaviorism, a psychological school focusing on observable actions rather than inner cognitive processes. It examines how external events can affect conduct and how these impacts can be utilized to form human activity. Behaviorism is based on reinforcement, punishment, and stimulus-response learning theory. Behaviorism aims to enable individuals to attain novel behaviors through rewards or penalties for their actions.
Explanation of How External Events Influence Behavior
Skinner was a significant contributor to the evolution of modern psychology, and his theories continue to be employed in numerous realms, such as education, animal training, and therapy for psychological complications, including phobias or anxiety disorders. He created multiple instructional techniques based on operant conditioning involving shaping methods that involve encouraging step-by-step approximations towards an anticipated action; token economies where positive activities are compensated with tokens which later can be traded for rewards; educational machines incorporating feedback after each answer from the student so they may observe their advancement over time.
Skinner’s efforts have had an extensive effect; they have been applied not only within psychology but also in areas like social science and instruction, significantly impacting teaching processes across many countries globally, even currently.
BF. Skinner and Reinforcement Theory
Importance of Reinforcement and Punishment in Behavior Shaping
BF. Skinner is widely accepted as one of the most essential psychologists in history, and his accomplishments have long influenced current psychology. He later became an eminent figure within behaviorism, a school of thought that concentrates primarily on observable actions instead of inner thoughts or emotions. His noteworthy contribution to psychology was reinforcement theory, which suggests that positive reinforcement teaches one how to achieve wanted behaviors and dodge unwanted ones.
Skinner’s influence on education has proven to be far-reaching, with numerous schools using his techniques in their teaching plans. The reasoning behind this technique is that when students are rewarded for achieving a task satisfactorily, they tend to become more motivated to repeat it later. This approach has had positive results in boosting student performance throughout all academic levels.
In addition to his work with reinforcement theory, Skinner developed other essential techniques, such as operant conditioning and behavior shaping through rewards or punishments (also called “schedules”). He wrote extensively about these theories in numerous books, including “Science and Human Behavior” (1953) and “Beyond Freedom & Dignity” (1971), which are considered two of the most influential texts ever written on human behavior, influencing not only academics but popular culture alike.
The legacy left by B.F. Skinner lives on today due to his pioneering theories and the B.F. Skinner Foundation, established in 1989. Each year, the foundation provides grants for research into behavioral sciences and awards bearing BF. Skinner’s name honor those who have made remarkable contributions within this field.
Operant Conditioning: Skinner’s Unique Approach to Learning Theory
Introduction to Operant Conditioning
His ground-breaking investigation on operant conditioning, termed “Skinner’s Distinctive Approach to Learning Theory,” redefined our grasp of learning and behaviorism, revolutionizing curriculum design in education.
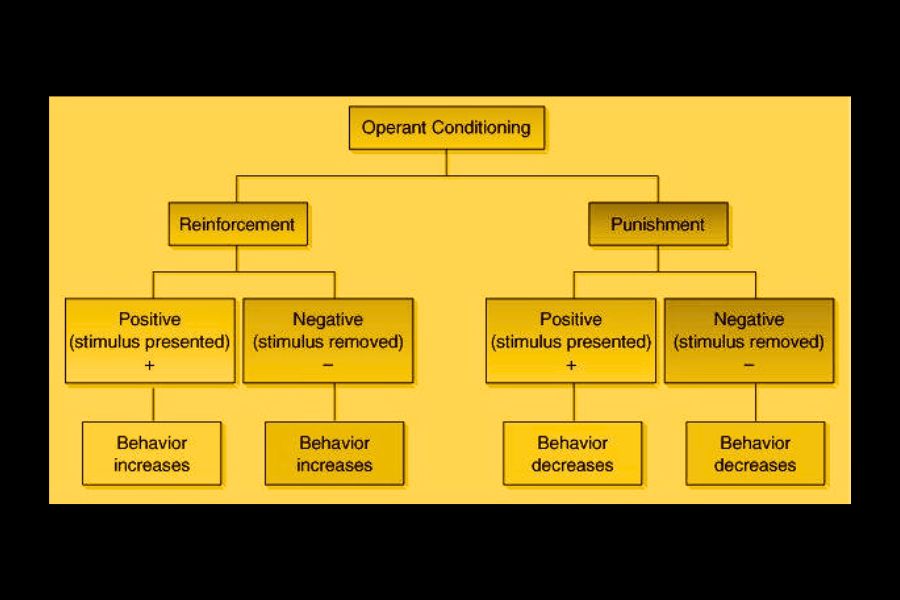
According to his postulation, organisms acquire knowledge through reinforcement for positive behavior and punishment when negative behaviors occur. Thus, desirable actions are more prone to being repeated while undesirable ones subside or are eradicated.
This form of learning was not wholly unprecedented; however, it was what distinguished BF. Skinner’s method was his comprehension of how this process occurred at a much more profound level than had been comprehended before.
Skinner’s Experiments With the “Skinner Box” and Positive Reinforcement
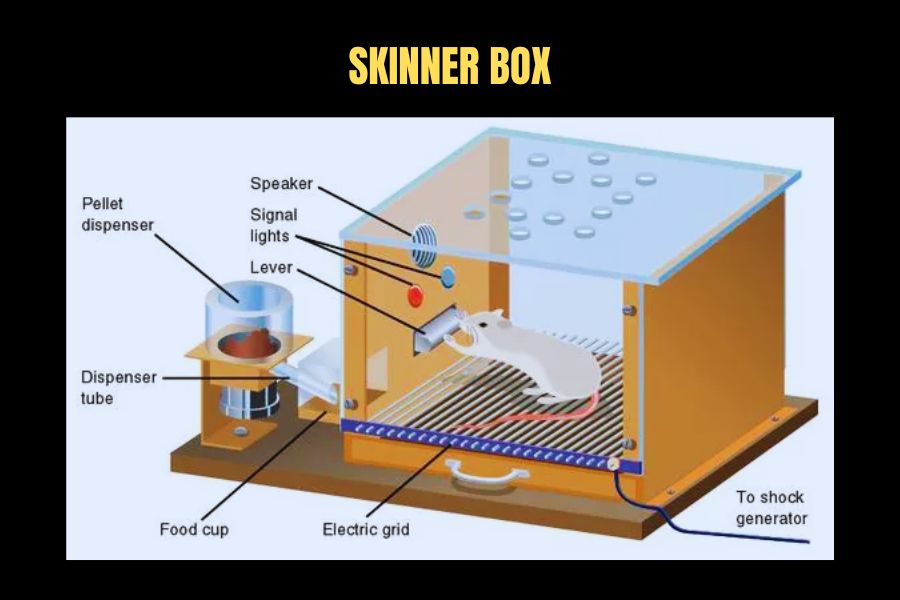
To gain an improved understanding of operant conditioning, BF. Skinner performed numerous trials with laboratory rats by putting them inside a box called ‘The Skinner Box.’ The container contained levers that, when pushed by the rat, would result in either reinforcement (in the manner of food pellets) or punishment (in the shape of a slight electric shock).
Based on his observations, he deduced that reward-based behavior was more likely to be repeated than punishment-based behavior. This idea has come to be known as ‘positive reinforcement theory.’
Applications of Operant Conditioning in Various Fields
Nowadays, operant conditioning is a cornerstone of contemporary psychological theories. Its effect can be observed across all aspects of human existence, from childrearing styles to professional training programs for employees.
Its fundamentals have even been adopted within the engineering field, wherein robots have been programmed with incentive systems analogous to BF. Skinner over half a century ago! Thus, had it not been for him, we would not have nearly so much understanding of our behavioral patterns – something everyone should note!
Radical Behaviorism: A Breakthrough Contribution to Psychology
Introduction to Radical Behaviorism as an Alternative to Psychoanalytic Theories
Prominent psychologist and behaviorist BF. Skinner’s most notable accomplishment was introducing Radical Behaviorism, a ground-breaking concept initially expounded in his influential literary work Verbal Behavior.
Emphasis on External Environmental Factors in Behavior
This approach constituted an innovative departure from traditional psychoanalytic theories, which emphasized inner mental processes as sources and drivers of human behavior, and instead emphasized external environmental factors.
Contrary to Sigmund Freud’s suppositions that human actions are propelled by concealed forces, including repression or hostility, BF Skinner held that behavior is caused by external provocations instead of inner motivations.
Radical Behaviorism seeks to explain the interaction between individuals and their surroundings and how this interaction influences their actions in the long run. It is accomplished through attentive observation and study of the solitary individual’s background and general outlines in human conduct across aggregates.
Applications of Radical Behaviorism in Different Disciplines
It likewise incorporates standards from biology, sociology, economics, linguistics, anthropology, and other scholarly fields into its exploration strategy to pick up a further comprehension of how different elements of an individual’s environment impact their behaviors over the long haul.
Moreover, Radical Behaviorism has been quite influential in reshaping our modern-day view of psychology and even infiltrating popular culture. More significantly, it has contributed substantially to advancing learning theory and is extensively utilized within educational practices and exceptional education programs.
This approach is also employed across animal training initiatives at zoos or aquariums, where animals are conditioned for displays or enrichment activities such as puzzles, which aim to amuse and develop cognitive skills.
Subsequently, its effectiveness with addiction issues like substance abuse disorders, including alcohol problems, has not gone unnoticed; through operant conditioning methods comprising rewards/reinforcement regimes (or punishments), unfavorable habits related to drug addictions, etc.., can be altered, resulting in individuals attaining superior control over their impulses which paves a road towards recovery instead of relapse.
Impact of BF. Skinner
Influence of Skinner’s Theories on Education and Curriculum Design
His theory of operant conditioning asserts that behavior is primarily influenced by its results, which has been embraced considerably across academic institutions as an effective means to influence student conduct positively. This approach has proven successful in helping students with behavioral issues or those battling academically.

Positive Behavior Intervention Support (PBIS) and Use of Incentives in Classrooms
Educational institutions frequently use incentives such as stickers and reward systems to encourage positive behavior and promote the desired conduct while reprimanding disruptive or inappropriate actions with time-outs or other appropriate penalties.
In addition, BF Skinner was a proponent of making learning enjoyable so that students could retain information more effectively.
Introduction of Active Learning Methods and Their Benefits
Active learning encourages students to think critically and analytically about the topic rather than just memorizing facts from textbooks or lectures, thus allowing them to cultivate a more profound knowledge of their studies while heightening enthusiasm for the subject matter.
Numerous educational establishments have adopted activities such as simulations, case studies, and role-playing in their classrooms to engage learners during lessons, thereby helping them comprehend concepts better and remember them for future use.
Furthermore, the impact of Skinner’s work has been far-reaching in transforming how curricula are created for elementary and secondary educational institutions across the globe. His methodology advocated that educators should prioritize teaching skills over merely focusing on content comprehension; this is due to his belief that it was essential for faculties not only to be aware of facts but also to possess abilities to apply information appropriately when faced with real-world scenarios outside academia.
This transition from memorization towards fostering skill-based learning grants learners from varied backgrounds an opportunity to gain eminence before enrolling in college or starting their professional careers, where possessing dexterity is paramount to achieving greatness.
Social Applications of Skinner’s Behavioral Theory in the 21st Century

Behavioral psychology has had a considerable influence on the realms of education and behavior alteration since its inception in the early 1900s. BF. Skinner, frequently regarded as the father of contemporary behavioral psychology, is often attributed with many ground-breaking theories and advances throughout his professional life. His concept of operant conditioning developed into an essential pillar for how humans comprehend behavior nowadays, and it has been employed extensively both within educational settings and daily living ever since its invention.
Regarding educational ramifications, BF. Skinner’s Theory has been employed to aid teachers in guiding students’ behavior by giving positive reinforcement for certain desired behaviors and negative reinforcement for undesirable conduct instead of punishing or randomly incentivizing them. This system is referred to as Positive Behavior Intervention Support (PBIS), which rewards good actions while helping to prevent bad behavior from emerging by teaching children what is expected from them and how they can meet those conditions without recourse to punishment or other forms of force.
Furthermore, beyond its utilization in education, BF. Skinner’s Theory has also had an influence on social applications such as parenting methods, addiction treatment programs, communication systems strategies used for stress management techniques, workplace dynamics, Etc., all based upon the idea that reinforcing desirable conducts will promote more beneficial outcomes whereas punishing unfavorable ones will discourage further poor results.
For instance, many addiction care plans take advantage of operant conditioning techniques like token economies, where individuals are given tokens each time they show preferred activities associated with recuperation (i.e., joining meetings or therapy sessions).
Legacy of BF. Skinner in Modern Psychology
Summary of Skinner’s Lasting Impact on Psychology and Cognitive Sciences
BF. Skinner, renowned as the father of modern psychology, was a revolutionary figure in the discipline whose influence continues to impact how we contemplate behavior and education even now. Burrhus Frederic Skinner (as his full name is acknowledged), born in 1904 in Susquehanna, Pennsylvania, earned recognition as one of the most eminent psychologists ever seen.
He produced several of conceptions of operant conditioning (learning through benefits and support). He investigated how humans learn from their habitat and how our conduct can be formed by external sources such as incentives or punishments. His pioneering effort laid the groundwork for additional progressions in psychology and cognitive sciences that are still being employed to comprehend why we do what we do and how best to adjust our activity to better ourselves and society.
Recognition and Awards Received During his Lifetime
BF. Skinner did receive several other significant awards and recognitions during his lifetime, including:
| APA Distinguished Scientific Contribution Award (1958) | Presented by the American Psychological Association for his distinguished scientific contributions to psychology. |
| Humanist of the Year (1972) | The American Humanist Association awarded him for his contributions to humanist thought and behaviorism. |
| Warren Medal (1991) | Awarded by the Society of Experimental Psychologists for his significant contributions to experimental psychology. |
| National Medal of Arts (2000) | President Bill Clinton presented the prize posthumously in honor of his contributions to the humanities and arts, notably his work in behavioral psychology. |
| Gold Medal of the American Psychological Foundation (1990) | Awarded posthumously for his distinguished career and contributions to psychology. |
Continued Relevance of His Work in Contemporary Psychological Theories
However, research continued until he died in 1990, aged 86. BF. Skinner’s oeuvre included numerous papers that were widely acclaimed; some pivotal titles include “The Behavior Of Organisms” (1938), “Science And Human Behavior” (1953) as well as “Verbal Behavior” (1957). These works contributed significantly to furthering understanding of psychology, learning theory, behaviorism, and language development, among other topics.
B.F. Skinner’s impact on popular culture, academic circles, and general readers is immense. With his scientific methods backed by empirical evidence rather than relying merely on speculation or anecdotal stories, he revolutionized human behavior studies at that time to become commonplace today. His literary pieces have been rendered into various languages, enabling non-native English individuals to appreciate his works!
Moreover, many school curriculums worldwide use aspects of operant conditioning techniques taught by B.F. Skinner; these positive reinforcement approaches help teachers manage their classroom better while giving students control over the learning environment, thus fostering a healthy relationship between educators & learners, owing greatly to understanding principles he propounded decades ago!
Publications of BF. Skinner
B.F. Skinner was a prolific writer and published numerous books, articles, and research papers throughout his career. Below is a list of some of his most notable publications:
| “The Behavior of Organisms” (1938) |
| “Walden Two” (1948) |
| “Science and Human Behavior” (1953) |
| “Verbal Behavior” (1957) |
| “Schedules of Reinforcement” (1957) |
| “The Analysis of Behavior” |
| “Contingencies of Reinforcement” |
| “Beyond Freedom and Dignity” (1971) |
| “About Behaviorism” (1974) |
| “Particulars of My Life” (1976) |
Criticisms Against the Work Of BF. Skinner
There are plenty of criticisms regarding the work of B.F. Skinner, coming from a variety of sources. Although some of these critiques can be considered valid, others may appear unjustified or even wrong-headed: certain commentators suggest that his behaviorism is too absolute and determined, whereas others highlight the ethical implications linked with his perspectives on human behaviors and their adjustment via reward and penalty schemes.
Discussion of Criticisms Regarding Deterministic Behaviorism
Regarding deterministic behaviorism, B.F. Skinner proposed that our conduct was primarily decided by a mixture of our environment (including both exterior and internal elements) and our heredity; this leaves little space for volition or selection in how we act or react to circumstances. This argument has been vigorously scrutinized by many philosophers who insist that free will is an integral part of being human, rendering Skinner’s view too simple to comprehend intricate issues such as morality or creativity.
Ethical Implications of Behavior Shaping Through Rewards and Punishments
Questions were raised about the ethics of Skinner’s views on human behavior due to their implications for controlling people’s actions through rewards and punishments rather than enabling them to make conscious decisions based on their moral code or beliefs; this has caused certain critics to query whether Skinner was advocating a form of “social engineering” which could result in oppressive regimes if employed without proper monitoring or regulation.
Concerns Over Animal Experimentation in Skinner’s Research
Furthermore, objections have been raised regarding that Skinner’s experiments often involved animals, which can be considered cruel depending on one’s perspective. It has naturally provoked resistance from animal rights activists who maintain these tests to be unethical irrespective of any possible scientific advantages they may provide.
Conclusion
B.F. Skinner is an iconic figure in psychology and beyond, widely regarded as one of the most influential psychologists ever. His trailblazing theories, educational journey, and renowned legacy have secured his place in history as a pivotal contributor to psychological research and theory.
Following completion of his undergraduate degree at Hamilton College, he then achieved accomplishment with obtaining a Ph.D. from Harvard University which occurred during 1931 during this period, John BF. Skinner developed many of his fundamental ideals that would eventually be acknowledged as behaviorism or radical behaviorism, an attitude towards psychology that concentrated on external behaviors instead of mental activities or states.
Eventually, this outlook acquired considerable fame due to its emphasis on how the environment is instrumental in defining one’s conduct rather than interior psychological conditions and impulses. One highly renowned experiment conducted by Skinner was known as the “Skinner Box,” which displayed how animals can acquire specific patterns based on reinforcement regimens (e.g., rewards).
The experiment entailed inserting a rat into a box where sustenance was located at one end; when the rodent extended its paw towards the food, it would be bestowed with a pellet – this consequently augmented that precise behavior after some time until becoming an instinctual reaction to reaching for nourishment when placed back in the compartment once more.
This trial brought forth proof of operant conditioning – wherein behaviors can be altered through reinforcement or punishment, which has been extensively implemented since then across areas such as education, animal training, parenting approaches, and so on.
B.F. Skinner developed a range of other significant hypotheses, including “schedules of reinforcement,” which revealed how different types of incentives (positive/negative) could be employed to form desirable behaviors; these discoveries have been profoundly helpful in fields such as animal training and behavioral therapy where positive stimulation is essential for achieving successful results.
Furthermore, he authored several books, Walden Two (1948), which studied utopian societies structured around principles resulting from his investigation findings; this book has since become renowned within social sciences due to its study of various social matters like educational reform and population control methods.
FAQS
Who was BF. Skinner and why is he significant in psychology?
BF. Skinner was an influential American psychologist who participated in the behavioral movement. He is best known for his work in behavioral psychology, particularly the theory of operant conditioning. He has contributed immensely to the development of psychology, education, and behavioral therapy.
What is BF. Skinner’s theory of operant conditioning?
According to Skinner’s theory of operant conditioning, learning occurs through the consequences of behavior. In positive reinforcement, the behavior is strengthened by adding a reward; in negative reinforcement, the behavior is strengthened by removing an aversive stimulus. Conversely, punishment lowers the probability of a particular behavior’s occurrence.
How did BF. Skinner’s “Skinner Box” experiment work?
“Skinner Box” was the name given to an experimental apparatus used to analyze animals’ behavior. It enabled Skinner to manipulate conditions and use reinforcements and punishments to study their controlled impact on behavior. This experiment was crucial in establishing the principles of operant conditioning.
What are some applications of BF. Skinner’s theories in modern psychology?
Skinner’s theories are applied in several disciplines, such as education, where strategies like positive reinforcement foster good behavior in classes. His work also supports most of the behavioral therapies used to treat conditions like autism and substance use disorders.
What criticisms have been raised against BF. Skinner’s work?
His theory has been criticized by many, especially after Skinner’s assertion that free will is an illusion. Others have questioned his ethics in animal experimentation and the social consequences of conditioning through reward and punishment.













